Key points from article :
Researchers at the University of Houston discovered a ‘Powerful Clinical Strategy’ for treating heart disease.
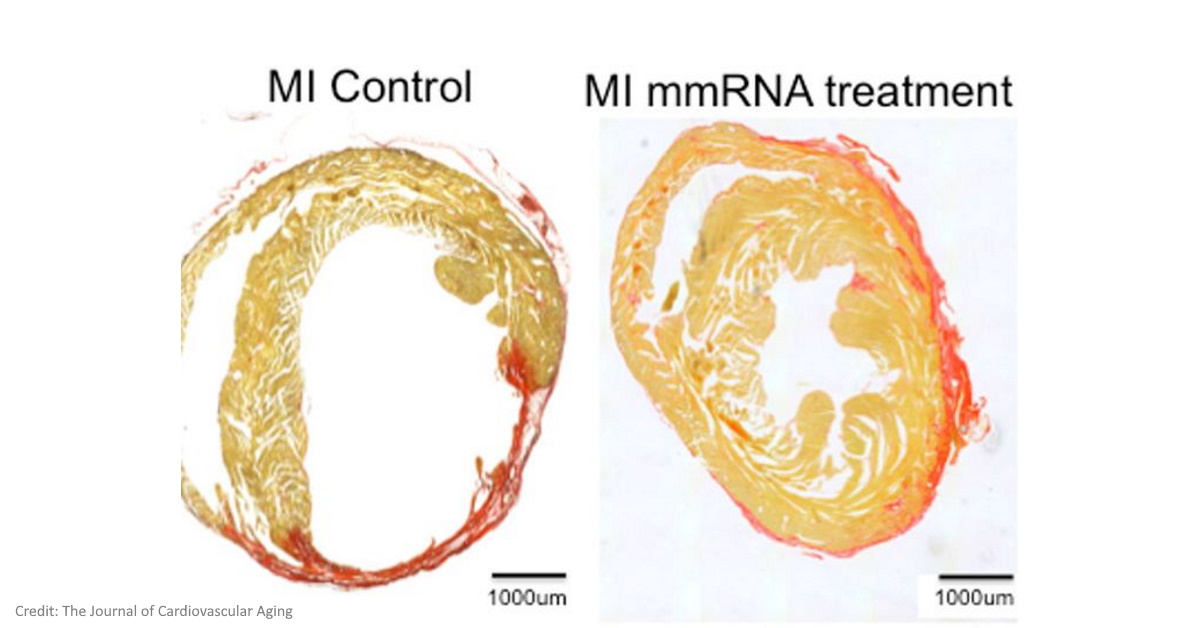
Not only repairs heart muscle cells in mice but also regenerates them following a heart attack, or myocardial infarction.
Uses synthetic messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) to deliver mutated transcription factors - to mouse hearts.
Two mutated transcription factors, Stemin and YAP5SA, work in tandem to increase the replication of cardiomyocytes.
Stemin turns on stem cell-like properties from cardiomyocytes and YAP5SA works by promoting organ growth.
Professor at the UH, Robert Schwartz said: "...hearts over the next month were repaired to near normal cardiac pumping function with little scarring.”
According to his Ph.D student added benefit is it disappears in a few days as opposed to viral delivery.
The findings are especially important because less than 1% of adult cardiac muscle cells can regenerate.
Research at University of Houston, published in The Journal of Cardiovascular Aging.