Key points from article :
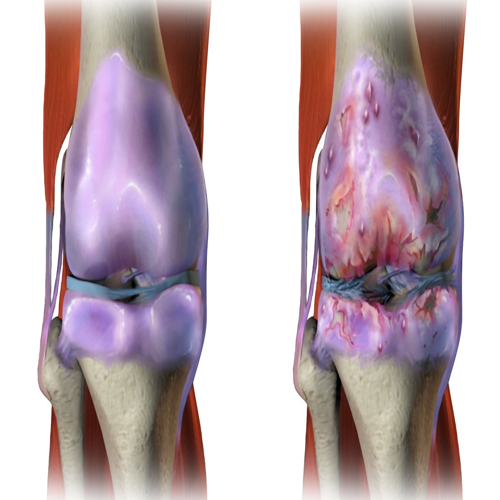
Method to regrow the cartilage that eases movement between bones, found.
Called articular cartilage, it is responsible for joint pains and arthritis.
Affecting more than 55 million Americans, or nearly 1 in 4 adults.
Existing treatment include a technique called microfracture.
This results in fibrocartilage --more like scar tissue than natural cartilage.
Researchers used a powerful molecule called bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2).
This is to initiate bone formation after microfracture, stopping midway with VEGF.
It restored mobility to osteoarthritic mice and significantly reduced pain.
Proof of principle also tested in humans through tissue transfer and was a success.
Main components of a potential therapy are approved as safe and effective by the FDA.
Research by Stanford School of Medicine, published in Nature Medicine.