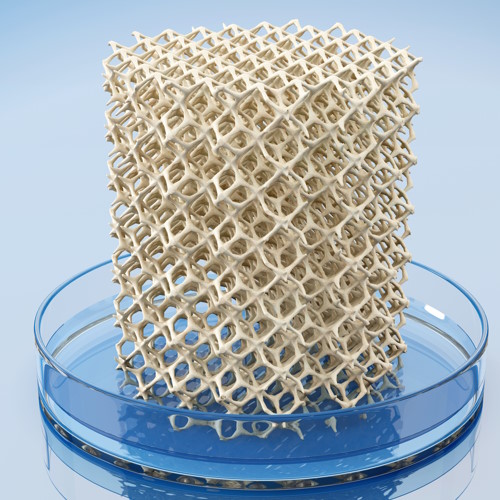
Key points from article :
Researchers used ink made from a natural bone mineral - hydroxyapatite, mixed with PLGA.
PLGA is a mineral-binding polymer that makes the implants elastic.
Printed bones are placed in the patient’s body where blood vessels infiltrate them and turn into real bones.
The procedure is cheaper but better.
In the future, the hospitals that will have 3D printers, hyperelastic bone ink could make individual implants.
Bone-mending technology developed at Northwestern University in Evanston.
The study was published in the journal Science Translational Medicine.