Key points from article :
Bioprinter could change completely the way musculoskeletal surgical procedures are performed.
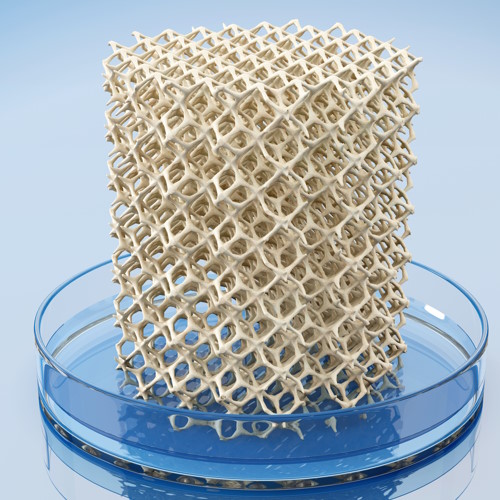
Surgeons deposit scaffolds, materials to support cellular and tissue growth directly into the defect sites.
Printer allows proper filling of the cavity with a fibrillar scaffold.
Fibrillar scaffolds mimic the properties of the existing tissue.
Bioprinted scaffolds have been created in vitro, but haven't been successfully used on an actual subject.