Key points from article :
Nanotechnology can improve the effectiveness of the cystic fibrosis (CF) antibiotic Tobramycin, by up to 100,000-fold.
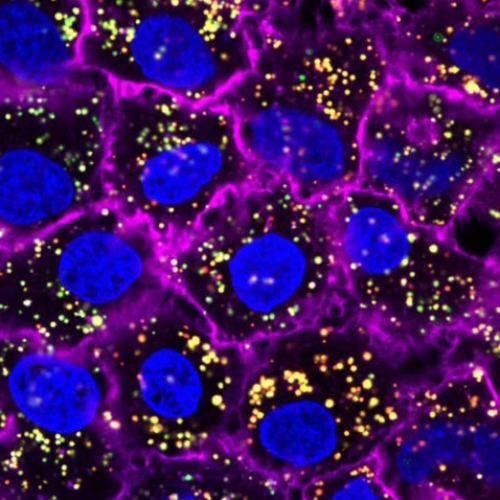
Treats chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections in severe CF—eradicating the infection in as little as two doses.
Tobramycin works by inhibiting the synthesis of bacteria and causing cell membrane damage.
Enhanced the Tobramycin with a biometric, nanostructured, lipid liquid crystal nanoparticle (LCNP)-based material.
"This could be a real game-changer for people living with CF," - Chelsea Thorn, co-author of the study.
Testing on a new lung infection model to showcase its unique ability to penetrate the dense surface of the bacteria and kill the infection.
"Our technology improves the performance of Tobramycin without increasing the toxicity of the drug," - Nicky Thomas, corresponding study author.
Currently entering pre-clinical trials and hopes to be on the market in the next five years.
Study by the University of South Australia published in the journal Small.